Specialised Echocardiography
What is Echocardiography?
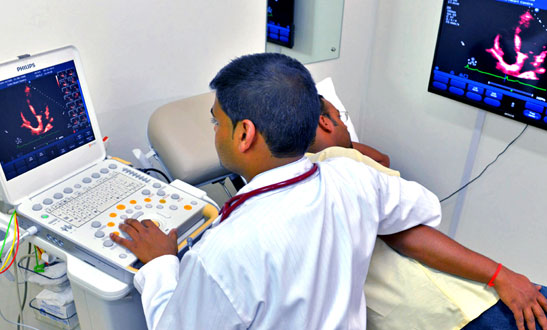
Echocardiography is an ultrasound of the heart.
The procedure is performed using a hand-held electronic device and gel applied to the chest, which enables ultrasound waves to travel and capture 2-dimensional, Doppler (blood flow) and 3-dimensional images of the heart.
The images allow the specialist to examine the structure, size, movement of the heart muscle, valves and the flow of blood through the chambers.
Why is it important to have a specialised Echocardiography procedure?
- Evaluate a heart murmur (abnormal heart sound)
- Diagnose the conditions of heart valves
- Find changes in the heart’s structure
- Assess motion of the chamber walls and identify any damages to the heart muscle after a heart attack
- Assess how different parts of the heart function in patients with chronic heart disease
- Determine if there is a collection of fluid around the heart
- Identify growths (infections) in the heart
- Assess and monitor birth defects
- Test blood flow through the heart
- Assess the extent of damage to the heart or major blood vessels caused by a trauma
- Test the functioning of the heart in connection with lung problems
- Assess chest pain, shortness of breath and palpitations
- Identify blood clots within the heart chambers that could lead to potential stroke
- Assess cardiac function during and after pregnancy
- Assess heart function prior to chemotherapy, surgery or medication intake
- Cardiac screening in diabetic patients
- Regular follow-up of patients who have undergone coronary artery by-pass graft (CABG), valve replacement or any other types of heart surgery
- Assess heart function in patients with high blood pressure
- Identify signs of ischaemic heart disease (insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle due to blocked arteries) in all patients with abnormal calculated cardiovascular risk scores obtained from blood test
- Cardiac assessment in Athletes
How do you prepare yourself for the scan?
- Clothing above the waist needs to be removed at the time of the scan, to facilitate the procedure. Gowns will be provided for ladies.
- No dietary restrictions are required prior to the scan.
- It is recommended that elderly/disabled patients are accompanied for their appointment.
How long does the scan take?
A specialised scan typically last between 45 and 60 minutes. However, the test may last for longer or less depending on the complexity of the case.
When will I get my scan report?
The Specialist will discuss the results with you after the scan. If treatment or further investigations are required, you will be routed to an appropriate specialist. The full study recorded on a CD and a diagnostic report of the findings will be made available to you for collection the following day at the centre.
Upcoming Services
Holter Analysis
In medicine, a Holter monitor is a portable device for continuously monitoring various electrical activity of the heart for at least 24 hours (often for 7 days at a time). The Holter's most common use is for monitoring heart activity (electrocardiography or ECG). Its extended recording period is sometimes useful for observing occasional cardiac arrhythmias (abnormal heart electrical activity), in symptomatic patients, which would be difficult to identify in a shorter period of time. For patients having more transient symptoms, a cardiac event monitor which can be worn for a month or more can be used.
Pediatric Echocardiography
Pediatric Echocardiography, commonly referred to as pediatric echo, is today the primary imaging tool in the diagnosis and assessment of heart diseases in infants and children. This specialised procedure, which uses high frequency ultrasound, is mainly used for the detection of congenital heart disease (heart defect present at birth). This technique is also used for the evaluation of murmurs and is an essential tool to evaluate the effectiveness of medical therapy and surgical treatments.
Echocardiography is an ultrasound of the heart. The procedure is performed using a hand-held electronic device and gel applied to the chest, which enables ultrasound waves to travel and capture 2-dimensional,
Doppler (blood flow) and 3-dimensional images of the heart. The images allow the specialist to examine the structure, size, movement of the heart muscle, valves and the flow of blood through the chambers.
Why is it important to have a specialised echocardiography procedure?
- Evaluate a heart murmur (abnormal heart sound)
- Diagnose the conditions of heart valves
- Find changes in the heart’s structure
- Assess motion of the chamber walls and identify any damages to the heart muscle after a heart attack
- Assess how different parts of the heart function in patients with chronic heart disease
- Determine if there is a collection of fluid around the heart
- Identify growths (infections) in the heart
- Assess and monitor birth defects
- Test blood flow through the heart
- Assess the extent of damage to the heart or major blood vessels caused by a trauma
- Test the functioning of the heart in connection with lung problems
- Assess chest pain, shortness of breath and palpitations
- Identify blood clots within the heart chambers that could lead to potential stroke
- Assess cardiac function during and after pregnancy
- Assess heart function prior to chemotherapy, surgery or medication intake
- Cardiac screening in diabetic patients
- Regular follow-up of patients who have undergone coronary artery by-pass graft (CABG), valve replacement or any other types of heart surgery
- Assess heart function in patients with high blood pressure
- Identify signs of ischaemic heart disease (insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle due to blocked arteries) in all patients with abnormal calculated cardiovascular risk scores obtained from blood test
- Cardiac assessment in Athletes
